
The rolling process is a process in which the friction between the rolled piece and the roll pulls the rolled piece into the roll with different rotation directions to produce plastic deformation. More than 90% of the plastic processing of metal materials, especially steel materials, is completed by rolling. It can be seen that rolling engineering technology plays a very important role in metallurgical industry and national economic production.
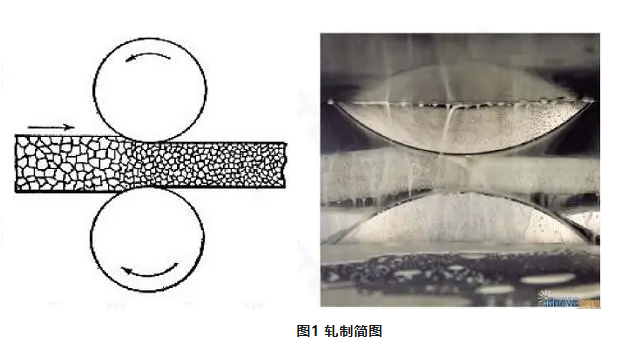
According to the product type, the rolling process can be divided into four basic types: plate and strip rolling, pipe rolling, profile rolling and rod and wire rolling. According to the production process can be divided into hot rolling and cold rolling process; According to the thickness, it can be divided into thin plate (thickness <4mm), medium plate (thickness 4~20mm), thick plate (thickness 20~60mm), extra thick plate (thickness >60mm, the maximum thickness of 700mm). In actual work, the medium plate and the thick plate are collectively referred to as "medium and thick plate".
Rolling process is the metal billet through a pair of rotating roller gap (various shapes), due to the compression of the rolling rod to reduce the section of the material, the length of the increased pressure processing method, which is the most commonly used production of steel production, mainly used to produce profiles, plates, pipes.
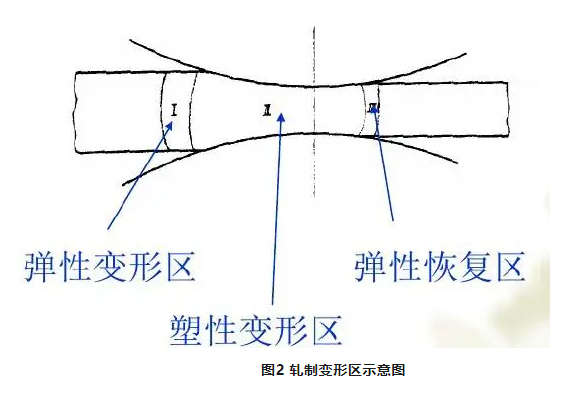
The part of the rolled part that deforms under the action of the roll is called the rolling deformation zone.
Simple and ideal rolling conditions: roll diameter is the same, the speed is the same, the roll is cylindrical rigid body, the rolling piece is uniform continuous, the rolling deformation is uniform, the rolling piece is flat.
Geometric deformation zone: the geometric zone between the contact surface of the rolled piece and the roll, that is, the area from the vertical plane of the rolled piece into the rolling rod to the vertical plane of the rolled piece out of the roll ACBD.
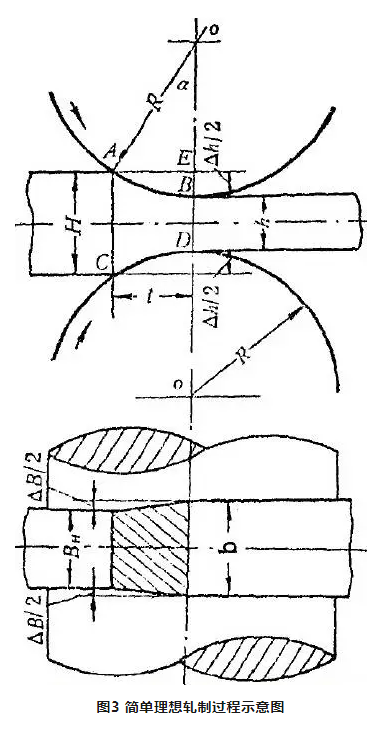
1) Bite Angle The Angle formed by the line between the first contact point of the rolled piece and the roll center and the line between the two rolls when the rolled piece is bitten into the roll.
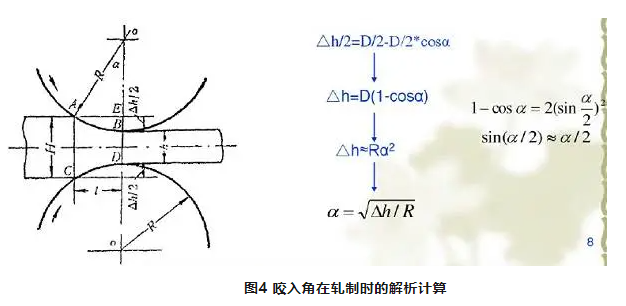
2) Deformation zone length The horizontal projection length of the contact arc between the rolled piece and the roll. When the two rolls are equal in diameter:
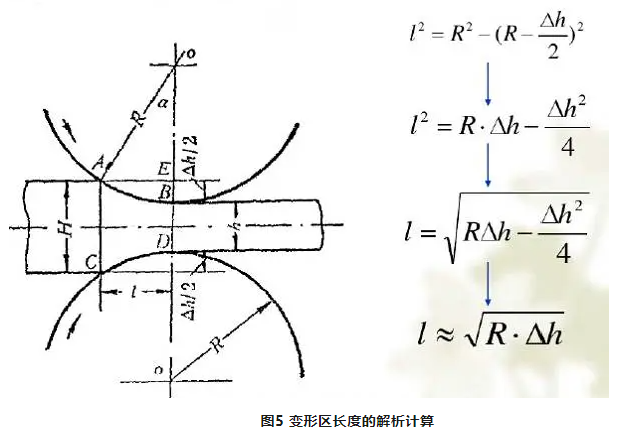
3) Contact area The horizontal projection area of the contact surface. The analytical formula is as follows:
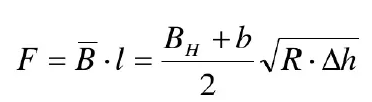
The formation of coarse crystal zone on strip surface is related to rolling state:
1) During rolling, due to the existence of friction, there is a difficult deformation zone in the contact part of the rolled part and the roll. When the rolling lubrication condition is not good, it is easy to produce a coarse crystal zone on the surface layer, and the lubrication can be improved by opening the cooling water between the frames.
2) The deformation distribution along the height of the rolled piece is uneven, and the surface layer deformation is small. When the reduction amount is not distributed properly, the surface layer deformation of the rolled piece is small, resulting in coarse crystals.
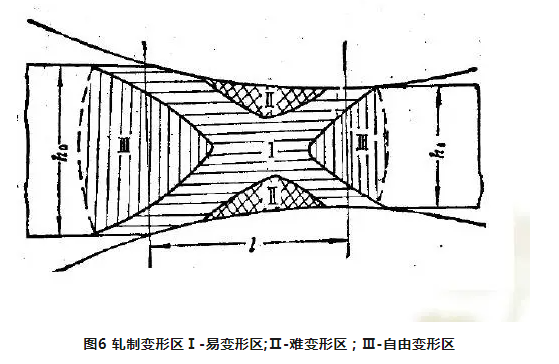
1) The distribution of deformation, stress and metal flow along the height of the rolled section is uneven.
2) In the geometric deformation zone, there is not only relative sliding but also adhesion on the contact surface between the rolled piece and the roll, and there is no relative sliding between the rolled piece and the roll in the adhesion zone.
3) Deformation occurs not only in the geometric deformation zone, but also outside the geometric deformation zone, and the deformation distribution is uneven, and the rolling deformation is divided into deformation transition zone, front slip zone, back slip zone and adhesive zone.
4) There is a critical surface in the adhesive zone, where the flow velocity of the metal is evenly distributed and equal to the horizontal speed of the roll. [1]
Asynchronous rolling is a kind of speed unequal rolling, the upper and lower work roller surface linear speed is not equal, in order to reduce rolling force; Therefore, it is also called differential rolling, also known as rolling. Asynchronous rolling is used to roll bimetal plate, which will cause the bending change of the rolled parts. Asynchronous rolling can adjust the bending curvature of the bimetal plate, and under the condition of the same asynchronous ratio, the thickness ratio of the two metal components can be obtained under a certain deformation degree. Asynchronous rolling is a new rolling process with many advantages. Using asynchronous rolling can greatly reduce the rolling force, so the equipment weight is light, the energy consumption is low, the mill deformation is small, the product precision is high; Reduce roll wear and intermediate annealing, and reduce production costs; Fewer rolling passes, high productivity; The rolling mill can be thick. Asynchronous rolling is not only suitable for cold-rolled strip, but also for hot-rolled plate, which is a promising production process. The main disadvantage of asynchronous rolling is that it is easy to cause mill tremor. [2]
Accumulative roll bonding (ARB) is two pieces of sheet material of equal size after the surface is degreased, work hardening, etc., stacked at a certain temperature and made automatic welding, and then repeated the same process repeatedly laminated, rolling and welding, so that the organization of the material is refined. The inclusion is evenly distributed and the mechanical properties of the material are greatly improved. [3]
Double drive rolling is often used in ring processing. Its basic working principle is basically similar to that of conventional ring rolling. The difference is that a driving torque is loaded on the core roll during double drive rolling, which makes the rotation mode of the core roll change from follow-up rotation to self-drive control rotation. Ring double drive rolling equipment is based on the conventional ring rolling equipment to change the core roller parts into the core roller with hydraulic drive rotation, which can realize the independent movement of the core roller. Under the rotating action of the drive roll and the core roll, the ring is continuously entered into the rolling pass formed by the drive roll and the core roll. Because the core roll operates independently and does not run with the ring, under the action of the friction between the roll and the ring surface, the rotation speed of the materials on the inner and outer surfaces of the ring does not match, as if the materials on the inner and outer surfaces of the ring are rolled, which increases the plastic deformation of the ring organization and causes continuous local plastic deformation of the ring. When the wall thickness is reduced, the diameter is enlarged, and the section profile is formed, the internal structure of the ring is improved due to large plastic deformation. When the diameter of the ring reaches the predetermined value through repeated multi-turn rolling, the outer surface of the ring touches the signal roller, the drive roller stops feed movement, and the rolling process of the ring double drive ends. In the rolling process, the guiding movement of the guide roller ensures the smooth rotation of the ring. [4]
【 Reference 】
[1] Zhan Meiyan. Rolling deformation theory of jet-deposited porous materials [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 18(6): 1-5
[2] Sun Jiquan. Development and Application prospect of asynchronous rolling Technology [J]. Angang Steel Technology, 2009, (5): 1-3
[3] Hou J. Research status and prospect of the preparation of particle reinforced metal matrix composites by cumulative rolling welding [J]. Materials Review A: Review, 2016, 30(2): 1-3
[4] Feng Shaogui. Effect of Double Drive Rolling Forming on Strain and microstructure Distribution of 5A02 aluminum alloy ring [J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2017, 42(6): 2-4