
Metal fatigue refers to the process of gradually producing local permanent cumulative damage in one or several places of materials and components under cyclic stress or cyclic strain, resulting in cracks or sudden complete fracture after a certain number of cycles. When the material and structure are subjected to repeated changes in the load, although the stress value has not exceeded the strength limit of the material, even lower than the elastic limit, the failure may occur, this phenomenon of material and structure failure under the repeated action of alternating load is called fatigue failure of metal.
In ordinary words, the metal under the continuous reciprocating load, will produce some small cracks on the metal surface, the metal surface cracks after accumulation, extended to a certain extent, will occur rapid and strong brittle fracture, in the occurrence of brittle fracture, the metal often does not bear more than the metal tensile/compressive strength of the load, the reason is that, The tensile/compressive strength of a metal is a value derived from static conditions, and the reason is that under alternating loads, the metal is more likely to reach the limit of strength and fatigue failure.
There are two main reasons for metal fatigue damage. On the one hand, after a series of processing, such as metal melting and casting, the metal structure inside the finished product is not uniform, which will lead to defects and internal stress inside the metal. After good heat treatment, the metal structure can be refined to eliminate most of the stress. The addition of various rare earth elements in the metal can improve the fatigue strength of the metal, and then play a role in improving the working life of the metal, on the other hand is the external factors, external factors can be summarized into three aspects, one is to distinguish according to the type of load, such as impact fatigue formed by the impact load on the surface, contact load, pits formed on the surface, pitting and other fatigue relief. Fretting wear fatigue, such as when the surface of two parts contact, the contact surface occurs a small amplitude of reciprocating relative movement, and then the surface of the part produces wear, oxidation, fatigue spalling and other forms of fretting wear fatigue, etc., according to the environmental temperature is divided into high temperature, low temperature, high temperature cycle, corrosion fatigue, etc., under high temperature conditions (metal melting point or recrystallization temperature above), As metal plasticity increases and hardness decreases, deformation and other problems are more likely to occur. Under low temperature conditions, metal plasticity decreases, brittleness increases, and metal is more prone to brittle fracture and other problems. As metal has the characteristics of thermal expansion and cold contraction, metal will produce internal stress under the conditions of high and low temperature circulation, thus causing fatigue damage to metal. Under the action of water vapor in the air, the metal surface will produce oxides, which will destroy the surface strength of the metal and make the corrosion area more prone to damage. According to the stress state, it is divided into single stress fatigue and multi-directional stress fatigue. Under the action of single stress cycle, the parts will get a life slightly lower than the limit of static load strength, and under the action of multi-directional stress, the parts are more prone to fatigue damage due to deformation.
Observed with a microscope, the fracture of metal fatigue damage is shown in the figure below.

The ductile fracture (such as tensile fracture) of the metal is shown in the figure below.

The brittle fracture section (such as broken) of the metal is shown in the figure below.
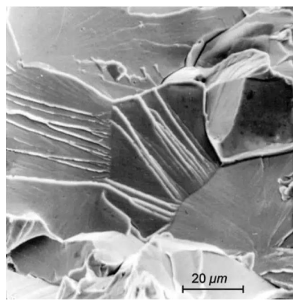
Among the three metal sections introduced above, the fatigue fracture section bears the least load, and the fracture occurs secretly and quickly, often starting from the defect part of the part, and then the part fails.
After understanding the formation conditions of metal fatigue, the next step is to explore how to find hidden metal fatigue. Since the beginning of the 19th century, when people discovered metal fatigue phenomenon, people have been exploring the causes of fatigue phenomenon. In the process of exploration, people have mastered a variety of detection methods, and there are 5 common detection methods: X-ray testing, ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, magnetic particle testing, penetration testing. Take X-ray detection as an example, through the X-ray penetration of the metal, the part of the metal with defects can penetrate more rays, and the part of the uniform density will reflect more rays, so in the imaging, the defect is darker, and the uniform density is brighter. In this way, we can more intuitively and quickly judge the distribution of defects inside the metal, so that we can avoid the occurrence of fatigue damage to a certain extent by avoiding the defect as a working area and strengthening the strength of the defect.